Burkina Faso
22.6
Population 2022 (Millions)
0.45
HDI Score
2021 (Max. 1)
52.5
SDG Score
2023
(Max. 100)
0.62
Gender Inequality
Index Score
(Max. 1)
98
Internet Inclusivity
Index 2022
(100 countries)
Overview
Projects

- Burkina Faso, Liberia, Sierra Leone, The Gambia
- March - May 2024
- Geographies of Inequalities
- Partner(s): UNDP Ethiopia (Funder)

- Burkina Faso, Senegal, Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA)
- October 2022 - March 2023
- Technology and Democracy
- Partner(s): Agence Française de Développement - AFD (Funder)
DPA developed a comprehensive ecosystem approach to address the multifaceted nature of disinformation in two West African countries. Recognizing the need to examine disinformation beyond social media, our methodology considered the interconnected networks of online influencers, traditional media, and groups weaponizing (dis)information for socio-political purposes. We also investigated the underlying economic, political, and social motivations driving the weaponization of disinformation by powerful groups or individuals, and allowing false or inaccurate narratives to be anchored in society. This approach enabled pinpointing the most effective intervention points within the (dis)information cycle in Senegal and Burkina Faso, providing valuable insights and recommendations, particularly concerning the role of bilateral aid agencies such as AFD.
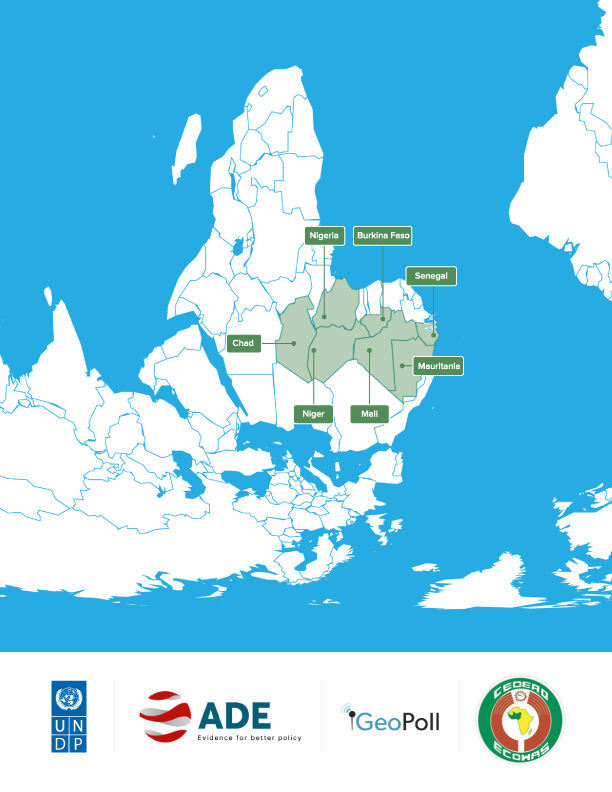
- Burkina Faso, Chad, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA)
- December 2020 - December 2021
- Resilient Livelihoods and Ecosystems
- Partner(s): ADE (Funder), Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), GeoPoll, UNDP Regional Hub for West and Central Africa (Funder)
In partnership with the UNDP Regional Office and the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), DPA and ADE conducted assessments of the socioeconomic impacts of COVID-19 and the role of disaster risk governance (DRG) in seven countries of the Western Sahel and Lake Chad Basin (Burkina Faso, Chad, Niger, Nigeria, Mali, Mauritania, and Senegal). The study analyzed the impacts of the pandemic on macroeconomic health, human development, political governance, peace, and social cohesion, as well as the role of DRG institutions at the regional and national levels. The assessment utilized mixed methods with qualitative and quantitative data collection to produce seven country-level analyses, a regional comparative study, and a policy brief.

- Bangladesh, Burkina Faso, Egypt, Ethiopia, Ghana, India, Kenya, Middle East and North Africa (MENA), Mozambique, Nepal, Sierra Leone, South Asia, Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA), Sudan, Uganda, Zambia
- June 2022- May 2023
- Data Feminism
- Partner(s): UNFPA, UNICEF (Funder)
The need to end child marriage and FGM has never been greater –without accelerated progress to end both of these harmful practices, millions of women and girls across the globe will continue to be in danger. DPA, in collaboration with UNICEF and UNFPA, conducted a comprehensive landscape mapping and review of key technology-based interventions to address child marriage and FGM across 13 countries in Africa and Asia (Bangladesh, Burkina Faso, Egypt, Ethiopia, Ghana, India, Kenya, Mozambique, Nepal, Sierra Leone, Sudan, Uganda, Zambia). During the second phase of the project, DPA carried out an in depth review of three selected interventions to better understand their effectiveness, key success factors, and potential areas for improvement.
The methodology proposed by DPA was based on intersectional feminist approach and an analysis integrating both quantitative and qualitative research methods, as well as traditional and non-traditional data sources collected at different stages of the study, underpinned by a participatory approach involving UNICEF, UNFPA, and other stakeholders.