Resilient Livelihoods
and Ecosystems
Why Resilient Livelihoods and Ecosystems
In an era of global transformation with overlapping and more frequent environmental, social and economic shocks and disasters, livelihoods and ecosystems, especially those in the Global South, are becoming increasingly fragile. How do we foster resilience in the face of these co-occurring shocks and complexity? At DPA our response is to improve evidence, knowledge and tools for policy-making at the nexus of crisis, conflict and climate change to strengthen the capacity of communities and ecosystems to cope with change and continue to develop.



Methods
DPA leverages mixed-methods data collection and analyses, evaluations, AI-based modeling, and participatory approaches for contextualized action-plans to strengthen resilience and produce stronger social protection systems.
Products
Crisis Impact Evaluations

- Senegal, Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA)
- June 2023 - February 2025
- Partner(s): WFP Innovation Accelerator (Funder)
After being selected to participate in WFP Humanitarian Innovation Accelerator Programme (HIAP), DPA has developed a project aimed at improving anticipatory action and response to climate-induced disasters in Senegal using OPAL for Humanitarian Action (OPAL4HA) by:
- Integrating diverse data sources such as call detail records (CDRs), earth observation (EO) data, qualitative data (surveys and interviews), official statistics, and user data to provide a holistic view of the crisis;
- Developing and testing the data model focusing on predictive analytics and pre-processed indicators of human displacement induced by climate shocks;
- Creation of a user-friendly query interface powered by Generative AI for timely insights;
- Automatic report generation to swiftly share progress with stakeholders; and
- Continuous refinement based on community feedback and targeted outreach to affected communities.
The project was presented at the United Nations STI Forum in May 2024 in New York, alongside other initiatives supported by HIAP. More details about the event can be accessed here.

- Liberia, Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA)
- June - December 2021
- Partner(s): European Union (Funder), FAO in Liberia (Funder), Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations - “FAO” (Funder), Government of Liberia
With the support of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) Liberia and the European Union, and in collaboration with the Government of Liberia, DPA assessed the socioeconomic impact of COVID-19 on agriculture, food security, livelihoods, and food systems in the country. The report combined key insights from the literature with primary and secondary data source analysis (including the use of microsimulations, multiple regression analysis, and key informant interviews). DPA designed a specific methodological framework to analyze the COVID-19 impacts from a holistic perspective.

- Egypt, Jordan, Middle East and North Africa (MENA), Morocco, Sudan, Tunisia
- May 2021 - May 2022
- Partner(s): Agence Française de Développement - AFD (Funder), Economic Research Forum (ERF)
In partnership with the Agence française de développement (AFD) and the Economic Research Forum (ERF), DPA produced a research paper investigating the potential associations between the socioeconomic impacts of COVID-19 on gendered mental health inequalities in the MENA region. The study adopted a mixed-methods approach, including a thorough literature review and quantitative data analysis using the Oaxaca-Blinder (OB) decomposition model. The results of this study were used to produce a policy paper with targeted recommendations to mitigate the impacts of the pandemic on women’s mental health and improve their social and economic well-being.
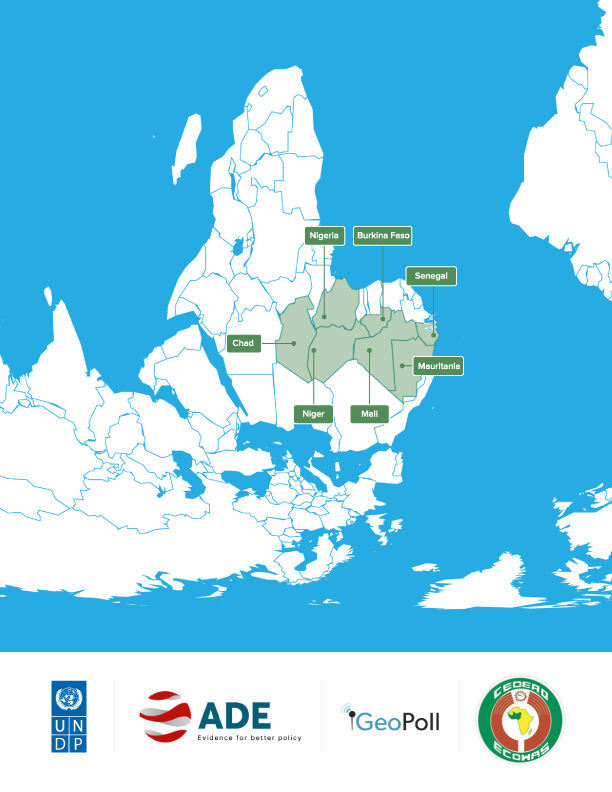
- Burkina Faso, Chad, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA)
- December 2020 - December 2021
- Partner(s): ADE (Funder), Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), GeoPoll, UNDP Regional Hub for West and Central Africa (Funder)
In partnership with the UNDP Regional Office and the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), DPA and ADE conducted assessments of the socioeconomic impacts of COVID-19 and the role of disaster risk governance (DRG) in seven countries of the Western Sahel and Lake Chad Basin (Burkina Faso, Chad, Niger, Nigeria, Mali, Mauritania, and Senegal). The study analyzed the impacts of the pandemic on macroeconomic health, human development, political governance, peace, and social cohesion, as well as the role of DRG institutions at the regional and national levels. The assessment utilized mixed methods with qualitative and quantitative data collection to produce seven country-level analyses, a regional comparative study, and a policy brief.
- Jordan, Lebanon, Middle East and North Africa (MENA)
- July 2020 - May 2021
- Partner(s): Central Administration of Statistics (CAS) - Lebanon, Department of Statistics (DoS) - Jordan, UN ESCWA (Funder)
Following an initial collaboration with UN ESCWA for the assessment “Leveraging Behavioral and Humanitarian Data Sources to Analyze the Development Challenges Faced by Syrian Refugees and Host Communities in Lebanon”, this project focused on utilizing non-traditional Big Data sources, such as social media and Google search data, to provide timely insights in crisis settings on key topics (economic indicators, access to food, sentiments around specific policies, etc). The DPA team collaborated closely with the Central Administration of Statistics (CAS) of Lebanon and the Department of Statistics (DoS) of Jordan and held several trainings and workshops around the project output.

- Liberia, Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA)
- June - October 2020
- Partner(s): ADE (Funder), UNDP Liberia (Funder)
In partnership with the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and ADE, the objective of this project was to conduct a rapid assessment of the socioeconomic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic (and its mitigation measures) in Liberia. The study was produced as part of a project analyzing the implications of COVID-19 on pre-existing macro and micro-economic, human development, and governance vulnerabilities. Based on the findings of the rapid assessment and in partnership with the UN Country Team in Liberia, a set of recommendations was developed to chart the roadmap for the short and long-term recovery process to build back better, leaving no one behind. This rapid assessment study aimed to provide the necessary evidence and inputs to inform and guide the relevant COVID-19 interventions and response efforts of the UN agencies, the Government, and other development partners.

- Equatorial Guinea, Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA)
- May - October 2020
- Partner(s): ADE (Funder), UNDP Equatorial Guinea (Funder)
In partnership with the United Nations Development Program (UNDP), ADE, and following the formal request of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, this project aimed to evaluate the initial effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the country. Through rapid macroeconomic and fiscal analysis, sectoral analysis (agriculture, tourism, ICT, education, and health), and analysis of socioeconomic vulnerability and expected impacts of the crisis on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), DPA produced a report with key recommendations to help the country recover and reduce vulnerability (applicable to subregions). DPA’s work focused on understanding the effects of COVID-19 and coordinating a response based on five pillars:
(1) Putting health first;
(2) Protecting people through social protection and basic services;
3) Promoting social cohesion and community resilience;
4) Supporting the macroeconomic response, and
5) Fostering multilateral collaboration.
All of this was done with the objective of advancing towards the SDGs, with the premise of leaving no one behind.

- Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA), Togo
- May - November 2020
- Partner(s): ADE (Funder), UNDP Togo (Funder)
In order to identify the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic in Togo, in partnership with the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and ADE, Data-Pop Alliance offered a synthetic analysis of the main impacts of the crisis in the country with a focus on the sector’s development priorities before the pandemic, using the most recent analyzes, studies and more recent data. The aim was to examine both quantitative and qualitative data available from the country; focusing on economy (SMEs and informal sector), social protection, basic services, food security; all with a transversal gender perspective. Particularly, the project’s report examined the situation before COVID-19 and identified its main effects and impacts; examined the content and conclusions of studies carried out on the impact of COVID-19, and raised the limits and/or potential deviations; analyzed how the limits in classical data can be complemented by data from alternative sources.
To read the report, click the button below (Available in French)
DownloadThe second part of this project focused specifically on conducting a mobility analysis during the COVID-19 pandemic in Togo. During this crisis, the Togolese government decided to introduce mobility restriction measures to prevent the spread of the virus. The resulting analysis used innovative data sources to characterize the changes in mobility patterns that followed the introduction of these measures. In this case, mobility data from Google and Facebook was used to measure changes during and after the implementation of mobility restrictions between February 15 and August 9, 2020, in each of the regions in Togo. In general, this study aimed to:
(1) Characterize the changes in mobility over time by type of mobility, particularly in residential areas and towards workplaces;
(2) Present the changes in mobility that resulted after curfew relief and lifting; and
(3) Understand mobility interconnections between regions. Limitations, assumptions, and recommendations were formulated based on the observations.
To read the report, click the button below (Available in French)
Download
- South Sudan, Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA)
- May - June 2020
- Partner(s): ADE (Funder), UNDP South Sudan (Funder)
With the support of the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and in partnership with ADE, this paper assessed both the direct and indirect effects of the pandemic in the country and identified implications for the donor community, including the UN System. First, it looked at macroeconomic and fiscal prospects, noting a dearth of options in the absence of sustained structural changes; then at the effects of COVID-19 on human development; the virus’s interplay with peacebuilding and state-building dynamics; and lastly, assessments of possible ways forward were discussed.

- Global
- October 2020
- Partner(s): Vodafone Institute for Society and Communications (Funder)
Building on the first publication “Sharing is Caring: Four Key Requirements for Sustainable Private Data Sharing and Use for Public Good”, this paper, developed in partnership with the Vodafone Institute for Society and Communications, looks at how digital technologies and data have been applied to fight COVID-19. The paper explored how the learnings from the first wave of the pandemic could provide an opportunity to use data more efficiently in the future to build back better.

- Maldives, South Asia
- May - July 2020
- Partner(s): National Bureau of Statistics Maldives, UNFPA Maldives (Funder)
In partnership with the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) Maldives and working closely with the National Bureau of Statistics of Maldives, this project sought to leverage Big Data sources, such as the mobile phone records (CDRs) and official statistics (household surveys) to provide data and study the effects of COVID-19 mobility restrictions on the population dynamics and mobility in the country. The study also analyzed the intricate relationships between attitudes, actual behavior and socioeconomic background in the Maldives by combining NBS survey data with movement patterns in a privacy-preserving manner. One of the main objectives of the project was to set a new benchmark for innovative application of mobile phone analytics in the region and beyond as a way to address population needs and monitor the impacts of shocks and stressors. The outputs of this projects included an analysis and policy paper with recommendations synthesizing key insights on the population dynamics obtained through CDR analysis and outlining applications towards advancement of five SDGs; and a capacity building-toolkit and ‘how-to” guide for using innovative data analytics methodologies and collecting and analyzing alternative data sources.
Vulnerability and Exclusion Assessments
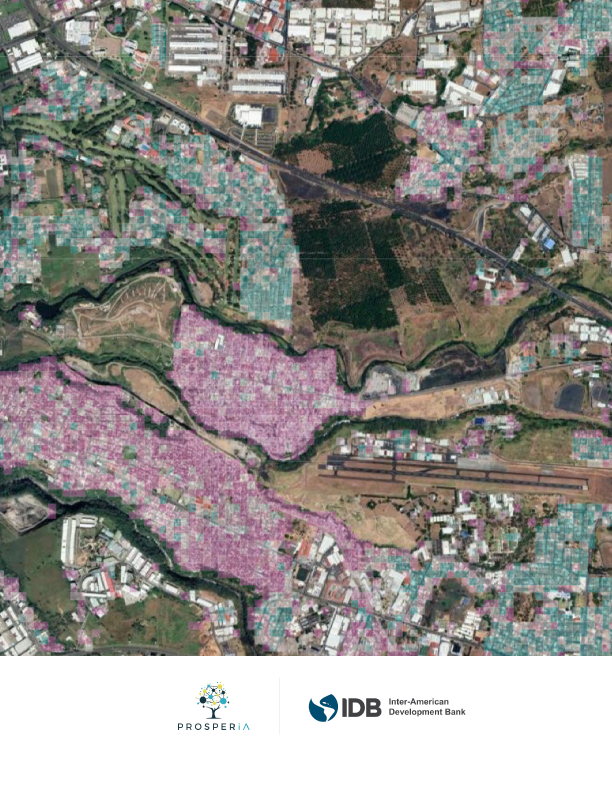

- Colombia, Dominican Republic, Honduras, Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC), Uruguay
- March 2022 - May 2023
- Partner(s): Inter-American Development Bank (Funder), ProsperIA

- Global
- April 2020 - January 2022
- Partner(s): UNDP (Funder)
This project, funded by UNDP, will support the Recovery Solutions and Human Mobility team in its conceptualisation of a new approach, articulating the Livelihoods and Economic Recovery offer, and reviewing, updating and documenting policies, programmes and tools on livelihoods and economic recovery that meet the current and future needs and expectations of UNDP Country Offices and partners in fragile contexts, crisis and post-crisis situations, exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic.

- Brazil, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Honduras, Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC)
- March - December 2020
- Partner(s): Inter-American Development Bank - Costa Rica (Funder), ProsperIA
Criteria, a project led by Prosperia with funding from the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB) and support from Data-Pop Alliance, is an interactive decision support system that empowers policy-makers to explore, analyze, and take decisions on the basis of a large number of potential designs and targeting schemes for social policies. Criteria uses microsimulations on survey and administrative data to visualize the expected poverty impact of policy alternatives resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as their associated costs.

- Colombia, Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC), Mexico, Namibia, Senegal, Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA)
- 2016 - 2019
- Partner(s): Agence Française de Développement - AFD (Funder), Cloud to Street, Flowminder, Harvard Humanitarian Initiative, MIT Media Lab, Overseas Development Institute
Four research papers were developed in collaboration with and funded by the Agence Française de Développement (AFD) between 2016 and 2019 under a joint program with Data-Pop Alliance and research partners (Cloud to Street, Flowminder, Harvard Humanitarian Initiative, MIT Media Lab, Overseas Development Institute) titled “Strengthening the evidence-base for leveraging Big Data to address global development challenges”. This research program and papers were designed with the following objectives and criteria in mind: to focus on various development challenges in different local contexts to ensure relevance; to work with trusted partners to ensure academic quality; and to both reflect and promote key determinants of sustainable development, including smoother, fairer, and safer access to data and stronger links between analysts, local decision-makers, and communities. Individually, these papers outlined specific cases and examples of how computational analysis of behavioral data (combined with other datasets) can paint a finer-grained, more complex, and dynamic picture of human reality than ‘traditional’ data allows. Collectively, they sketched the contours of a world where public decisions, in the form of policies and programs, might someday be designed, implemented, and evaluated using the best available data and approaches.
Future of Livelihoods Lab

- Middle East and North Africa (MENA), Morocco
- November 2022 - October 2023
- Partner(s): Moroccan Ministry of Economy and Finance, UNDP Morocco (Funder)
This project, supported by UNDP Morocco and the Moroccan Ministry of Economy and Finance, aimed to improve official statistical methodologies by using Big Data, in order to improve the timeliness and reliability of progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals. Additionally, this project contributed to strengthening the Moroccan digital ecosystem by improving the design, implementation, and monitoring of fair public policies, and informing better investment decisions towards achieving g the SDGs. Our organization conducted a benchmark study and developed three pilot publications to monitor priority indicators for sustainable development in Morocco: mental health (target 3.4) using Google Trends data; water stress (indicator 6.4.2) using earth observation; and ICT skills (indicator 4.4.1) using data collected through an online survey in Facebook.

- Liberia, Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA)
- November 2023 - July 2024
- Partner(s): UNDP Liberia (Funder)

- Senegal, Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA)
- September 2023 - December 2025
- Partner(s): Belmont Forum (Funder), IDEMA, Initiative Prospective Agricole et Rurale (IPAR), Orange-Sonatel, Paris-Lodron-University Salzburg (PLUS), Swedish Research Council (Funder)
Climate change (interlinked with humanitarian crises and other economic and health factors) could have led to internal resettlements, international migration, and other (new) forms of human mobility. However, the empirical link between various climatic conditions and migration outcomes was highly contested, and, to date, no unified theoretical approach had adequately captured the complexity and contextual dependency of climate-induced migration. To address this gap, CLIMB sought to develop a holistic approach which would allow a better understanding of the mechanisms and pathways underlying the climate-migration nexus, and to predict temporal-spatial mobility patterns in Africa and beyond. Specifically, we investigated how climate change might intersect with conflicts, poverty, and epidemics, among other adversities, and how these forces might operate in tandem in driving human migration, with a special focus on Africa.
OPAL

- Liberia, Sierra Leone, Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA)
- May 2022 - March 2023
- Partner(s): UNDP Liberia (Funder), UNDP Sierra Leone (Funder)
This study, supported by the UNDP’s Country Offices in Liberia and Sierra Leone, developed a deep understanding of the existing informal social protection mechanisms and community development needs in the borderlands of Sierra Leone and Liberia. DPA adopted an inductive ethnographic approach consisting of qualitative methods complemented with quantitative data collection to identify borderland community needs and trends, covariate shocks faced and coping mechanisms, as well as the inclusion and exclusion factors. The outputs and findings of the study informed government and UNDP programmatic interventions aimed at strengthening the resilience of these communities.