Mauritania
5.0
Population 2023 (Millions)
0.5
HDI Score
2022 (Max. 1)
58.2
SDG Score
2023
(Max. 100)
0.6
Gender Inequality
Index Score
(Max. 1)
N/A
Internet Inclusivity
Index 2022
(100 countries)
Overview
Situated in northwestern Africa, where the Sahara Desert meets the Atlantic Ocean, Mauritania is a vast and sparsely populated country marked by arid landscapes, nomadic traditions, and deep-rooted cultural heritage. Historically inhabited by Berber and Arab peoples, Mauritania became part of various trans-Saharan trade routes, connecting sub-Saharan Africa with North Africa and the Mediterranean world. The country was colonized by France in the early 20th century and gained its independence in 1960. Today, Mauritania faces a range of social, economic, and political challenges. Though rich in natural resources such as iron ore and fisheries, much of the population lives in poverty, with limited access to education, healthcare, and clean water. Deep inequalities persist, including the legacy of hereditary slavery, which, though officially abolished, still affects segments of society. In recent years, the country has contended with issues of governance, human rights, and the threat of regional insecurity spilling over from the Sahel. Despite these difficulties, Mauritania maintains a strong cultural identity shaped by its diverse communities, Islamic traditions, and long-standing resilience.
Projects
- Partner(s): ADE (Funder), Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), GeoPoll, UNDP Regional Hub for West and Central Africa (Funder)
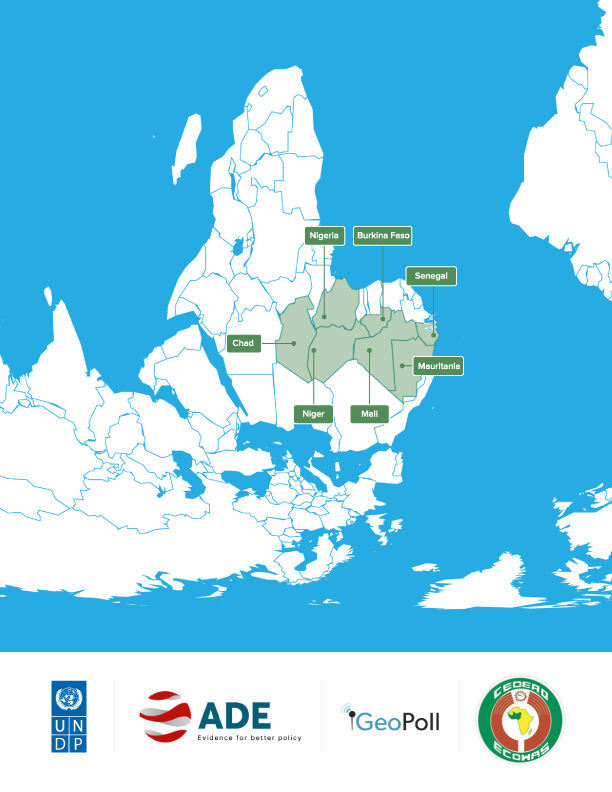
In partnership with the UNDP Regional Office and the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), DPA and ADE conducted assessments of the socioeconomic impacts of COVID-19 and the role of disaster risk governance (DRG) in seven countries of the Western Sahel and Lake Chad Basin (Burkina Faso, Chad, Niger, Nigeria, Mali, Mauritania, and Senegal). The study analyzed the impacts of the pandemic on macroeconomic health, human development, political governance, peace, and social cohesion, as well as the role of DRG institutions at the regional and national levels. The assessment utilized mixed methods with qualitative and quantitative data collection to produce seven country-level analyses, a regional comparative study, and a policy brief.

- Partner(s): Ministère de la Transition Numérique, de l'Innovation et de la Modernisation de l'Administration, World Bank (Funder)
The Mauritania component of the West Africa Regional Digital Integration Program (WARDIP-Mauritania) is expanding access to broadband and digital services through the development and integration of the country’s digital markets with those of the West African region. The project focused on 3 key elements for the integration of digital technologies at the regional level: the connectivity market, the data market, and the online market. This involved:
(1) Continuing the efforts begun under the WARCIP-Mauritania Project to expand connectivity, lower cost, and improve quality of service;
(2) Enabling the secure exchange, storage, and processing of data across borders, and supporting regional deployment of and access to data-based services and innovation;
(3) Expanding access to and delivery of public and private online services; and
(4) Establishing transparent and secure e-commerce at the regional level.